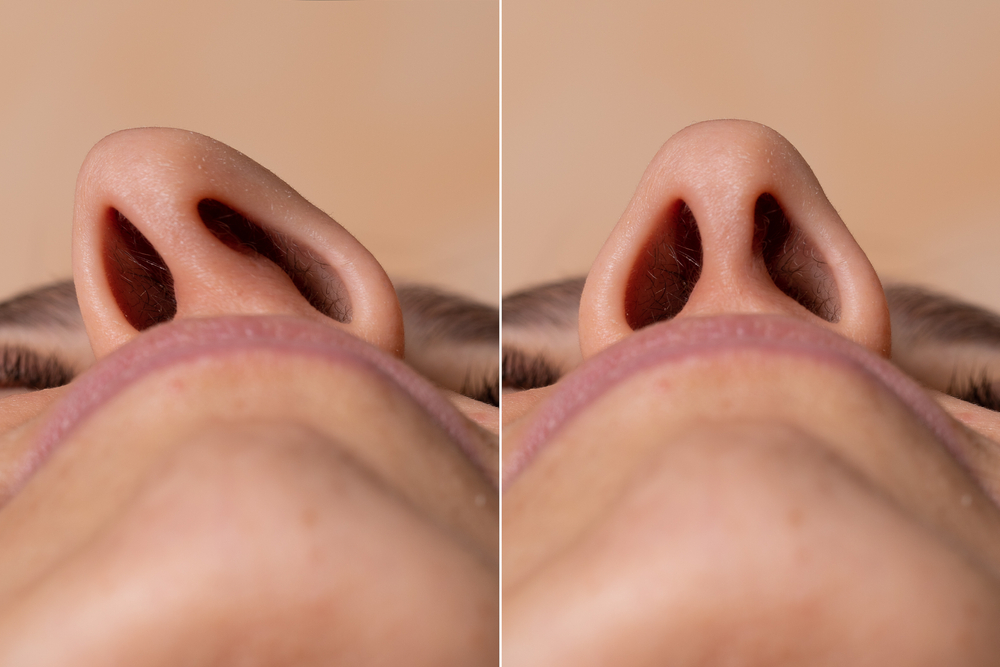
If you notice that a single nostril consistently feels more restricted than the other, you share a common experience. An off-center septum is a common condition that can affect breathing, sleep, and overall comfort, and it often occurs without people realizing the cause of their symptoms.
Grasping the symptoms of a deviated septum is the first step in choosing between basic symptom management and professional treatment.
What Is a Deviated Septum?
Anatomically, the septum is the thin partition of cartilage and bone separating the two sides of the nose. Ideally, it sits in the center of your nose. When it’s shifted to one side, it’s called a deviated septum.
The origin of a deviated septum may be congenital, or it may develop because of a nasal injury later in life. A minor shift might not cause problems, whereas a significant shift can create a major obstruction in the nose.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Deviated Septum
The presence of a deviated septum alters nasal airflow, resulting in a collection of signs that range from mild to intense.
Difficulty With Nasal Airflow
A primary indicator of this condition is the difficulty to draw breath through either nasal passage. You might identify these signs:
- A perpetual sense of nasal fullness
- The ability to breathe with greater ease through one nostril
- Nasal issues that flare up during allergic reactions or infections
Long-Term Congestion Issues
While cold-related stuffiness is temporary, the congestion from the deviation usually:
- Does not resolve with the changing seasons
- Doesn’t fully respond to allergy medications
- Presents as a permanent anatomical issue rather than temporary inflammation
Sleep Disruptions and Snoring
A blockage in the nasal airway may lead to:
- Regular snoring patterns
- Resorting to breathing through the mouth during sleep
- Disturbed or non-restorative sleep
For certain patients, a deviated septum intensifies other sleep-disorder breathing conditions.
Frequent Nosebleeds
The imbalance of air can cause the mucosa of the nose to become irritated and dehydrated. Such dryness frequently leads to:
- Frequent episodes of nasal bleeding
- The formation of dry tissue within the nostril
- Sustained tenderness within the nasal cavity
Comparing Allergic Symptoms to a Deviated Septum
Symptoms of the deviation often mimic allergies, making it important to understand the distinct causes.
Signs of a Structural Deviation:
- Are frequently limited to a single nostril of the nose
- Remain constant throughout all seasons
- Fails to resolve fully with allergy medications
Symptoms Related to Allergies:
- Generally cause congestion across the whole nasal airway
- Are often accompanied by itchy eyes and sneezing
- Often improve with antihistamines or nasal sprays
When these two issues coexist, they can create a compounding effect on nasal discomfort.
When to Address Your Deviated Septum
Professional medical advice should be sought when:
- You struggle to breathe clearly through your nose every day
- Rest and snoring issues start to impact your health
- Episodes of nosebleeds start to happen more often
- Congestion doesn’t improve with medication
- Your daily comfort is impacted by nasal issues
An evaluation can help determine whether symptoms are structural, inflammatory, or a combination of both.
Septoplasty: A Treatment Option for Deviated Septum
Clinical septoplasty is the standard procedure designed to straighten the nasal partition and enhance airflow. This option is usually explored if symptoms continue despite the use of non-surgical therapies.
The Benefits Of Septoplasty can include:
- Significantly enhance nasal airflow
- Eliminate persistent nasal fullness
- Improve the sleep environment by stopping snoring
- Prevent further episodes of chronic nosebleeds
A professional consultation will help decide if surgery is the best path for your unique situation.
Your Journey to Relief from a Deviated Septum
While a deviated septum is quite prevalent, it is also highly manageable with the right care. When congestion and snoring disrupt your life, discovering the source of the problem is the primary step to relief.
We can help clarify what’s contributing to your symptoms and guide you toward options that improve comfort, airflow, and quality of life. Call our specialists today if you are ready to address your deviated septum and reclaim your quality of life.